13 April, 2020
On January 1, 2020, Foreign Investment Law of the People's Republic of China (hereinafter referred to as “Foreign Investment Law”) and Implementing Regulations of the Foreign Investment Law of the People's Republic of China (hereinafter referred to as “Regulations”), officially came into effect. They are of epoch-making significance in the field of foreign investment in China in that they bring about a new system that requires pre-entry national treatment plus a Negative List for the administration of foreign investment. In order to better implement such system, the Measures for Foreign Investment Information Reporting (hereinafter referred to as the “Measures”) also came into effect on the same day.
The purpose of this article is to introduce and interpret the main contents of the Measures, and analyze and discuss some of the practical issues that may arise during the information reporting process. We aim to provide guidance for foreign investors and foreign investment enterprises to better fulfil their information reporting obligations.
1. An Introduction to the Newly Established Foreign Investment Information Reporting System
The Measures comprises of six chapters, namely (1) General Principles; (2) Reporting Entities, Contents and Methods; (3) Information Sharing, Publication and Correction; (4) Supervision and Administration; (5) Legal Liabilities and (6) Supplementary Provisions. There are 35 articles in total. In addition to Foreign Investment Law, Regulations and Measures, the Ministry of Commerce, the State Administration for Market Regulation and other relevant departments have issued a series of supporting documents, which jointly form the new foreign investment information reporting system. In the first part of this article, we will introduce the laws and regulations related to the new system, as well as their main content.
A. Related Laws and Regulations
|
Document |
Date of effect |
Promulgating Institution |
Main Contents |
|
Foreign Investment Law of the People's Republic of China |
January 1, 2020 |
National People's Congress |
As a basic law on foreign investment, the Foreign Investment Law clearly lays the foundation for the establishment of a foreign investment information reporting system in Article 34, and stipulates the penalties for violating the information reporting obligations in Article 37. |
|
Implementing Regulations of the Foreign Investment Law of the People's Republic of China |
January 1, 2020 |
State Council |
Article 38 of the Regulations further clarifies that foreign investors or foreign investment enterprises shall submit investment information to the relevant commerce department. Meanwhile, Article 39 sets out the principles of the information reporting system: government departments should follow the principles of necessity, efficiency and convenience in collecting information; on the other hand, information submitted by investors or enterprises shall be authentic, accurate and complete. |
|
Measures for Reporting of Foreign Investment Information |
January 1, 2020 |
Ministry of Commerce; State Administration for Market Regulation |
The Measures further details and clarifies the rules regarding the system of foreign investment information reporting in Foreign Investment Law and the Regulations and regulates the information reporting in to four aspects: reporting, sharing, supervision and penalties. |
|
Announcement on Matters Relating to Foreign Investment Information Reporting (Announcement No. 62 of the Ministry of Commerce) |
|
Ministry of Commerce |
This provides specific guidance for foreign investors and foreign investment enterprises regarding reporting entities and procedural matters. |
|
Notice by the State Administration for Market Regulation, the Ministry of Commerce and the State Administration of Foreign Exchange on the Proper Handling of the Work of the Reform of "combining multiple reports into one integrated report" for Annual Reports (Guo Shi Jian Xin [2019] No. 238) |
December 16, 2019 |
State Administration for Market Regulation; Ministry of Commerce; State Administration of Foreign Exchange |
This Notice is specific to annual reports. It requires the integration of items that were previously reported annually to commerce departments and foreign exchange departments into annual reports to market regulation department, i.e. a new system of "combining multiple reports into one integrated report". |
|
Announcement by the Ministry of Commerce, the State Administration for Market Regulation and the State Administration of Foreign Exchange on the Submission of Annual Reports for 2019 Foreign Investment Information Reporting (Announcement No. 72, 2019 of the Ministry of Commerce) |
January 1, 2020 |
Ministry of Commerce; State Administration for Market Regulation; State Administration of Foreign Exchange |
This announcement provides practical guidance on specific matters regarding the 2019 annual foreign investment information reporting, including the timing, method, remedies and progress inquiries for the report. |
|
Notice by State Administration for Market Regulation on Implementing the Foreign Investment Law and the Proper Handling of the Work of the Registration of Foreign-invested Enterprises (Guo Shi Jian Zhu [2019] No. 247) |
January 1, 2020 |
The State Administration for Market Regulation |
The State Administration for Market Regulation shall assist the Ministry of Commerce in implementing the foreign investment information reporting system. It also confirmed that submitting foreign investment information reports is not a pre-condition for the registration of foreign investment enterprises. |
B. Reporting Entities of Investment Information
Article 2 of the Measures provides that “if foreign investors carry out investment activities in mainland China directly or indirectly, foreign investors or foreign investment enterprises shall submit investment information to the relevant commerce departments in accordance with these measures”. What kind of natural persons and entities are included in the definition of "foreign investors" and "foreign investment enterprises" here? And who is responsible for the reporting obligations? Based on the analysis of the abovementioned laws, regulations and administrative documents, we have summarized the reporting entities as follows:
|
Reporting Entity |
Analysis |
|
A foreign investor who directly invests in the establishment of a company or partnership enterprise, or purchases the equity interest in a non-foreign investment enterprise (including banking, securities, insurance and other financial industries) in mainland China (the “foreign direct investors”) |
According to Article 9 of the Measures and Article 1 of the Announcement on Matters Relating toForeign Investment Information Reporting (hereinafter referred to as “Announcement No. 62 of the Ministry of Commerce”), such foreign direct investors shall submit initial reports. |
|
Foreign enterprises (including territories) that engage in production and operational activities in mainland China Foreign enterprises (including territories) that set up a residential representative office which engages in production and operational activities in Mainland China (collectively referred to as the “foreign enterprises”) |
According to Article 1 in Announcement No. 62 of the Ministry of Commerce, foreign enterprises shall submit initial reports, change reports and annual reports. |
|
Investment companies, venture capital enterprises and partnership enterprises with investment as their core business which are set up by foreign investors for reinvestment in mainland China (collectively the “foreign-invested enterprises for reinvestment purposes”) |
According to Article 1 in Announcement No. 62 of the Ministry of Commerce, foreign-invested enterprises for reinvestment purposes shall submit initial reports, the same as foreign direct investors. |
|
Foreign investment enterprises (including enterprises set up in mainland China by foreign-invested enterprises for reinvestment purposes) |
According to Article 11-14 of the Measures, investment enterprises shall submit change reports, annual reports and dissolution reports. |
|
Ordinary enterprises which are set up in mainland China by foreign investment enterprises via reinvestment (excepting foreign-invested enterprises for reinvestment purposes) |
According to Article 4 in Announcement No. 62 of the Ministry of Commerce, the initial reports, change reports, dissolution reports and annual reports of enterprises set up by foreign investment enterprises (including multi-tier investments) in mainland China shall be shared by the State Administration for Market Regulation with the Ministry of Commerce, and will no longer need to be submitted separately by the relevant enterprises. |
|
Investors from Hong Kong, Macau and Taiwan, and overseas Chinese |
According to Article 33 of the Measures, the Measures shall apply, mutatis mutandis, to investments by investors from Hong Kong, Macau and Taiwan, and overseas Chinese in mainland China. |
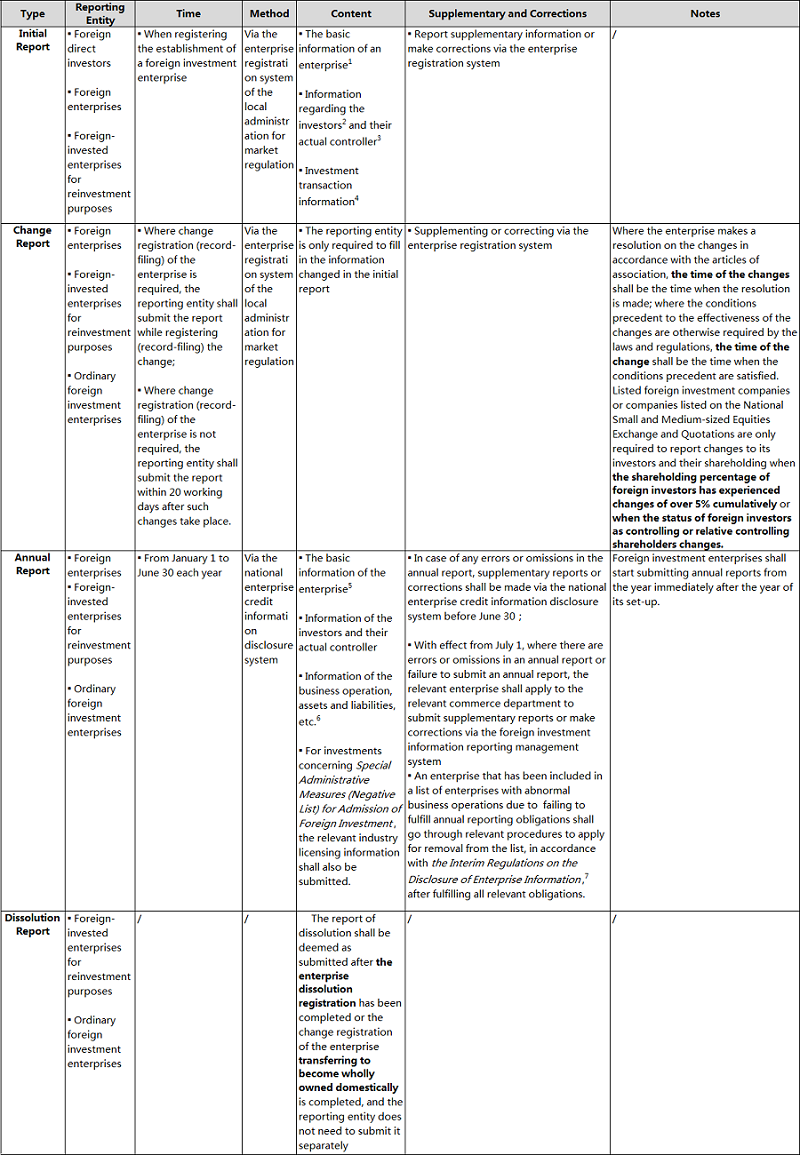
C. Types of Investment Information Reports
According to the Measures, there are four types of information reports: Initial Reports, Change Reports, Annual Reports and Dissolution Reports. The following table details the reporting entities, reporting times, reporting methods, reporting content, supplementary reports and corrections involved in each report.
D. Penalties for Violating Information Reporting Obligations
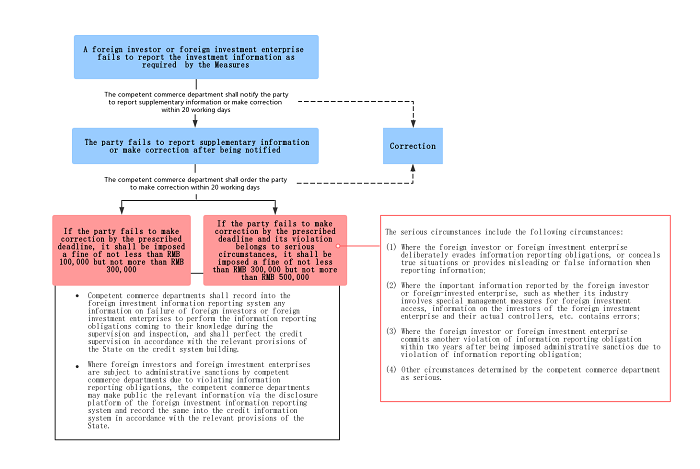
According to the Measures, the reporting entity shall report investment information in a timely, authentic, accurate and complete manner, without any false or misleading information or omission of important information. At the same time, the reporting entity also has the obligation to supplement and correct the report where necessary. Meanwhile, the relevant commerce department may carry out supervision and inspection measures based on the complaints and suggestions of the relevant departments or authorities. For ease of understanding, the legal consequences that one may face in different stages and for different degrees of violation when failing to perform the information reporting obligations correctly are shown as follows:
Compared with the draft of the Measures8, the final Measures provides more opportunities and longer times for the correction of the violation of the information reporting obligations. For example, if a foreign investor or foreign investment enterprise fails to report the investment information as required by the Measures, there is an added procedure that the reporting entity shall be notified by the relevant commerce departments to make supplementary reports or corrections within 20 working days; if it fails to do so within the above time limit, another time limit kicks in for the commerce department to further order it to correct. The time limit has also been extended from the 15 days specified in the draft version to 20 working days in the final version. Additionally, the administrative penalty of warning has been removed from the final version. These "lenient" administrative penalty procedures may have taken into account the fact that the foreign investment information reporting system is not a strict pre-approval or filing procedure and it may also be designed to provide a buffer for foreign investors and foreign investment enterprises to adapt to this new system.
2.Interpretation of the Key Features regarding the Measures
The following is a summary of the key features regarding the Measures to help readers grasp the key points that foreign investors and foreign investment enterprises need to pay attention to in fulfilling their information reporting obligations.
A.Consolidating and Optimizing the Processes for Information Reporting
According to the Joint Press Conference by the Ministry of Commerce and State Administration for Market Regulation on Issues Concerning the Measures, the initial reports, change reports, and dissolution reports by foreign investments shall be carried out simultaneously with the set-up, change and dissolution registration of the administration for market regulation, and the annual reports shall be submitted at the same time and through the same channels as the annual reports of the administration for market regulation. Foreign investors and foreign investment enterprises do not need to submit the same information to two departments separately9. In order to facilitate reporting entities in submitting the reports, the foreign investment information reporting system of many provinces and cities has been embedded in the enterprise registration system. Reporting entities can choose to use either the website of the local administration for market regulation or the website of the government service to register on the internet and report information regarding foreign investment in a "one-stop" manner. Some provinces and cities still retain independent websites for reporting foreign investment information for reporting entities to use10. As the enterprise registration system is designed and maintained by local administration for market regulation, there are some differences in the operation of the different local systems in practice. However, there is no need to submit or upload materials for foreign investment information reporting, and the registration authority does not review the report. The reporting entity can simply follow the instructions, log into the system, check the boxes and enter the relevant information.
B.Ordinary Foreign Investment Enterprises do not need to Submit Additional Information Reports for Domestic Reinvestment to set up Enterprises
According to Article 28 of the Measures, if a foreign investment enterprise (except for foreign-invested enterprises for reinvestment purposes) invests in the set-up of an enterprise (including multi-layer investments) in mainland China, the relevant information shall be forwarded to the relevant commerce department by the administration for market regulation after the registration and submission of the annual report information to the administration for market regulation, and the above-mentioned enterprise does not need to submit a separate information report. We understand that this means in the case of reinvestment by ordinary foreign investment enterprises, if the information in the initial report (the basic information of the enterprise, information of the investors and their actual controllers, information of investment transactions, etc.) submitted by its upper-layer foreign investors has not changed, the ordinary foreign investment enterprises are not required to submit the change report.
C.Disclosure Requirements for Actual Controllers
According to the Measures, both the initial report and the annual report require the submission of information regarding investors and their actual controllers. In the sample form of the initial report and the change report by foreign investments (hereinafter referred to as the "Sample Report Form") attached to Announcement No. 62 of the Ministry of Commerce, the definition of actual controllers and their control methods are also elaborated by way of information listing.
In the Sample Report Form, the actual controllers are grouped into the following categories:
-
Foreign listed companies
-
Foreign natural persons
-
Foreign government agencies (including government foundations)
-
International organizations
-
Domestic listed companies
-
Domestic natural persons
-
Domestic state-owned / collective enterprises
-
Others
In addition, the Sample Report Form also specifically lists the following three types of control methods:
1.Directly or indirectly holding more than 50% of the shares, equity, property shares, voting rights or other similar rights and interests of the enterprise;
2.Directly or indirectly holding less than 50% of the shares, equity, property shares, voting rights or other similar rights and interests of the enterprise, however:
(1)having the right to directly or indirectly appoint more than half of the members of the board of directors or similar decision-making bodies of the enterprise;
(2)having the ability to ensure that its nominees have more than half of the seats on the board of directors or similar decision-making bodies of the enterprise; or
(3)holding enough voting rights to have a significant impact on the resolutions of the board of shareholders, the shareholders assembly or the board of directors and other decision-making bodies.
3.Being able to determine the operation, finance, personnel or technology of the enterprise through contracts, trusts or other means.
The Ministry of Commerce and the State Administration for Market Regulation further clarified in their response11 to the relevant questions about the Measures that foreign investment enterprises reinvesting (this includes multi-tier investments) in China are also within the scope of foreign investment. In the past, there have been many areas that have adopted the policy of indentifying the ultimate actual controller for foreign investment. For example, when reviewing the proportion of foreign investment of enterprises applying for ICP licenses in the fields of value-added telecommunication services, the mainstream opinion of the relevant departments is that the review should identify the ultimate actual controller. Now, under the framework of Foreign Investment Law and the Measures, the foreign investment component of domestically reinvested enterprises by foreign investment enterprises in all fields will be reviewed and the ultimate actual controller will be identified. Therefore, under the foreign investment information reporting system, no matter how many tiers of enterprises the foreign investors set up in China, they should truthfully report the investors and the ultimate actual controller of the investors. This is also reflected in the online foreign investment information reporting systems in different provinces and cities.
D.Remedial Measures for Failing to Submit Annual Reports on Time
According to Article 14 of the Measures, the timeframe for foreign investment enterprises to submit annual reports is from January 1 to June 30 of each year. According to the Announcement of the Ministry of Commerce, the State Administration for Market Regulation and the State Administration of Foreign Exchange on Carrying out the Annual Report on Foreign Investment Information in 2019, from July 1, 2020, if there is any failure, error or omission in the annual report, the foreign investment enterprise shall apply to the relevant commerce department for a supplementary report or correction through the foreign investment information report management system. That is to say, even after July 1, there still exists certain remedial channels. However, considering that the Announcement also stipulates that if an enterprise is included in the list of abnormal businesses due to its failure to fulfill the obligation of annual reporting, it shall go through the relevant procedures in accordance with the Provisions of the Interim Regulations on Enterprise Information Disclosure (see part I, table 3 of this article). Therefore, we suggest that foreign investment enterprises should ensure to submit the annual reports before June 30 each year.
E.Attention should be paid to the Adverse Consequences of a Violation of the Information Reporting Obligations
In addition to the administrative penalties introduced in the first part of this article, according to the Measures, violations of information reporting obligations will be recorded in the foreign investment information reporting system, and those who are subject to administrative penalties will also be publicized on the disclosure platform of the foreign investment information reporting system, and included in the credit information system in accordance with the relevant provisions. According to the Interim Regulations on Enterprise Information Disclosure, enterprise credit information will be considered as an important factor in government procurement, project tendering and bidding, state-owned land use right grants and others, and enterprises listed on an abnormal operation or serious violation list will be restricted or banned in accordance with the law. In addition, due to the wide usage of the enterprise credit information system, enterprises that are subject to administrative penalties for violating information reporting obligations may also be negatively affected in bidding, financing and trading. Therefore, we suggest that foreign investors and foreign investment enterprises attach great importance to and strictly fulfill the obligations of information reporting.
Additionally, it should be noted that Article 21 of the Measures clearly stipulates that any citizen, legal person or other organization may report to the relevant commerce department any violation of the Measures by foreign investors or foreign investment enterprises. In this environment of all-round societal supervision, the risk becomes even greater if one intends to circumvent or superficially perform its duty of information reporting.
F.Effective Date and Exceptions of the Measures
The Measures came into force on January 1, 2020. Based on the principle of non-retroactivity and pursuant to paragraph 6 of Announcement No. 62 of the Ministry of Commerce, the Measures is only applicable to foreign investment enterprises established or changed after the effective date. However, Announcement No. 62 of the Ministry of Commerce has made transitional provisions on the following situations: if a foreign investment enterprise (that does not concern Special Administrative Measures (Negative List) for Admission of Foreign Investment) has completed the establishment registration at the administration for market regulation before December 31, 2019, or the matters under the provisions of Article 6 and Article 7 of the Provisional Measures on Administration of Filing for Establishment and Change of Foreign Investment Enterprises (now repealed) have changed, but the establishment filing or change filing of foreign investment enterprises has not yet been submitted, then it could still be filed via “the comprehensive foreign investment management system” before January 31, 2020. That is to say, if there is a change before December 31, 2019, but the change is not filed in accordance with the old procedures before January 31, 2020, then the change report needs to be submitted in accordance with the Measures (since the filing of foreign investment enterprises is a precondition of the establishment registration before December 31, 2019, the exception will not occur in the establishment registration scenario).
3.Practical Issues to be Further Clarified
Although there are detailed instructions as to how foreign investors and foreign investment enterprises can fulfill their obligations of information reporting in the Measures and other relevant administrative documents, we believe that there are still some practical issues relating to information reporting that need further guidance from the relevant regulatory authorities during the implementation of the Measures. Below are a few practical issues that we believe need to be clarified:
A.The Relationship between Information Reporting and Enterprise Registration
Although the State Administration for Market Regulation has repeatedly stressed in the Notice of the State Administration for Market Regulation on Implementation of the Foreign Investment Law for Proper Handling of Foreign Investment Enterprise Registration and reaffirmed in its answers to the questions from reporters that the submission of foreign investment information report is not a precondition for the registration of enterprises with foreign investment, we have noticed that in practice, in some provinces and cities, one can only submit an online registration after completing the foreign investment information reporting procedures, before going further to the relevant administration for market regulation for an on the spot enterprise registration12. Subjectively, local government departments may intend to facilitate foreign investors and foreign investment enterprises in their process of reporting, however in reality, it is not completely consistent with the legislative purpose of placing information reporting as a matter for post-event supervision. We suggest that the relevant local administration for market regulation should improve the enterprise registration system as soon as possible, to bring it in line with the purpose of the legislation and effectively reduce the burden on enterprises.
B.The Scope of Information Disclosure
According to Article 18 of the Measures, investment information submitted by foreign investors or foreign investment enterprises which should be disclosed or agreed to by foreign investors or foreign investment enterprises to disclose according to the Provisional Regulations on Enterprise Information Disclosure, will be disclosed to the public through the national enterprise credit information disclosure system and foreign investment information reporting system. However, it is worth noting that according to the Notice of the State Administration for Market Regulation, the Ministry of Commerce and the State Administration of Foreign Exchange on Properly Handling the Work of the reform of "combining multiple reports into one integrated report" for the Annual Reports, the items in the annual reports of the relevant commercial department and the foreign exchange management department are added on top of the existing items in the annual reports submitted to the market regulation department, but the items added in annual reports should not be disclosed to the public (which seems inconsistent with the provisions of the Measures). Therefore, we suggest that further clarification be made as to which contents in the foreign investment information report should (or may) be disclosed, in accordance with the Measures and the Provisional Regulations on Enterprise Information Disclosure.
C.The Scope of Foreign Enterprises (including territories) that Engage in Production and Operational Activities in Mainland China that are Obliged to Submit Information Reports
According to the first paragraph of Announcement No. 62 of the Ministry of Commerce, apart from the set-up of companies and partnerships by foreign investors, if foreign enterprises (including territories) engage in production and operational activities or set up a permanent representative organization in China, it shall also submit information reports. How to accurately understand the scope of “foreign enterprises (including territories) engaging in production and operational activities in China” is key to determine whether the relevant foreign enterprises (including territories) have an obligation of information reporting.
According to the Administrative Measures on the Registration of Enterprises of Foreign Countries (including territories) Engaging in Production and Operational Activities in mainland China (revised in 2016, hereinafter referred to as “the Administrative Measures of Foreign Enterprises Engaging in Operational Activities in China”), registration is required for foreign enterprises (including territories) to engage in the following production and business activities in China:
-
The exploration and exploitation of on-shore and off-shore oil and other mineral resources;
-
contracting for projects such as the construction or renovation of housing or civil projects or the installation of lines, pipelines or equipment;
-
contracting for or accepting commission for the operation and management of a foreign investment enterprise;
-
the establishment of a foreign bank branch in China;
-
other production and operational activities permitted by the State.
The issuing authority of the Administrative Measures of Foreign Enterprises Engaging in Operational Activities in China is the State Administration for Industry and Commerce (now the State Administration for Market Regulation), which is different from the issuing authority of Announcement No. 62 of the Ministry of Commerce which is the Ministry of Commerce. Therefore, whether the scope of "production and operational activities" of foreign enterprises (including territories) mentioned in Announcement No. 62 of the Ministry of Commerce should be interpreted the same way as in the Administrative Measures of Foreign Enterprises Engaging in Operational Activities in China still needs to be clarified by the commerce department.
D.The Identification of Actual Controllers
In the Sample Report Form for foreign investments initial and change reports attached to Announcement No. 62 of the Ministry of Commerce, the actual controller is defined by listing the control methods (see Item C of Part II above for more details), but uncertainties still exist in the determination of the actual controller in certain scenarios in practice, such as: (1) for foreign investors who are overseas listed companies, is it enough to trace it to such listed companies or does it need to be traced all the way to the actual controller of such listed companies? (2) in scenarios where the voting rights of a company are decentralized without a controlling shareholder or even a relative controlling shareholder, or where the minority shareholders “acted in concert” to control the company, how should we ascertain the information for such actual controllers? These problems may need to be specifically addressed by the relevant commerce departments in future practice.
E.Assets Appraisals in Mergers and Acquisitions for the Set-up of Foreign Investment Enterprises
According to the Sample Report Form, foreign investors that set up foreign investment enterprises via merger and acquisition need to provide the basic information of the transaction, including the evaluation of the equity interest/asset value in question. We understand that this requirement is based on Article 14 of the Provisions on Merger and Acquisition of Domestic Enterprises by Foreign Investors ([2006] No. 10) (hereinafter referred to as "Decree 10") issued in 2006 by the Ministry of Commerce. The parties to the merger and acquisition shall determine the transaction price on the basis of the appraisal results of the assets appraisal institution on the equity interest to be transferred or the assets to be sold. However, for merger and acquisition transactions between domestic enterprises, except for those involving state-owned assets, there is no mandatory appraisal requirement for the equity interest or assets to be acquired.
According to the principle of "equal treatment of foreign investment" (except investment within the scope of the Negative List) set forth by the Foreign Investment Law, and the provision of Article 24, that unless the laws and administrative regulations stipulate otherwise, the legitimate rights and interests of foreign investment enterprises shall not be impaired, their obligations shall not be increased, and the conditions for market access and exit shall not be set. Obviously, after the implementation of the Foreign Investment Law, if there is no justification based on the laws or administrative regulations, the relevant provisions in Decree 10 (only a departmental rule) which distinguish between domestic and foreign investment shall no longer be effective. Therefore, we suggest that the relevant commerce department clarify the concrete scenarios which require the submission of appraisal reports in the information report (for example, whether it is only applicable to the acquisition of state-owned equity interest or assets), so as to avoid increasing the unnecessary transaction costs to foreign investors. In addition, we notice that the financial audit report numbers also need to be provided in the column of “value appraisal” in the Sample Report Form. Since the definition of asset appraisal and audit is different13, does the "financial audit report" here refer to the asset appraisal report? This issue needs to be further clarified.
F.Whether Foreign Enterprises Engaging in Production and Operational Activities in China Need to Submit Dissolution Reports
According to Announcement No. 62 of the Ministry of Commerce, foreign enterprises engaging in production and operational activities in China need to submit initial reports, change reports and annual reports. However, for the dissolution report, the announcement only stipulates that the relevant information of foreign investors or foreign investment enterprises does not need to be submitted separately; instead it shall be shared by the State Administration for Market Regulation with the Ministry of Commerce. According tothe Administrative Regulations on the Registration of Representative Offices of Foreign Enterprises and the Administrative Measures of Foreign Enterprises Engaging in Operational Activities in China, foreign enterprises engaging in production and operational activities in China need to apply for dissolution for the cancellation of representative offices or the expiry of business licenses, etc. The Measures and other administrative documents don’t specify whether the dissolution information herein is also directly forwarded to the relevant commerce department by the market regulation department, or should be submitted separately by the relevant foreign enterprise. Therefore, we suggest that the relevant department make further clarification in this regard.
4.Conclusion
The foreign investment information reporting system is an important part of China's latest foreign investment legal system, and on the one hand greatly simplifies procedures and lessens the time constraints for foreign investment to enter China, but on the other hand, it raises the standards for foreign investors and foreign investment enterprises for information disclosure with regard to their investment, production and operational activities in China, particularly in terms of punctuality, authenticity, accuracy and completeness; the failing of which will lead to severe risks both in terms of administrative penalties and corporate credit worthiness. Foreign investors and foreign investment enterprises need to attach great importance to these new regulatory changes and actively adapt to and comply with them. At the same time, there are practical issues that need to be further clarified in the implementation of the foreign investment information reporting system. It would be helpful if the relevant regulatory authorities provide timely and specific advice for foreign investors and foreign investment enterprises to fulfill their information reporting obligations accurately and smoothly.
ZHENG, Yu, Partner, Jun He
zhengy@junhe.com
1.Includes basic registration information, the type of business, method of investment, information of the industries for encouraging foreign investment, information of employees, etc.
2.Includes identity information and the type of investor, capital contributions, transfers of equity/property, etc.
3.Includes identity information and the type of the actual controller, methods of actual control, ultimate actual controller, etc.
4.Includes basic information and the results of asset appraisals of the merged or acquired entity, related-party transactions, etc.
5.Mainly includes basic registration information, business scope, license for accessing relevant industries, enterprise attributes, the total workforce at the end of the previous year, salaries of employees, number of valid patents, etc.
6.Mainly includes audited financial information and data of the previous year.
7.The applicant shall submit the application form, originals of its business license, photocopies of the duplicates of its business license sealed by affixing the official seal, the originals and duplicates of resident identity cards of the legal representative (or the principal), supporting materials for the application and other documents to the market regulatory departments, and the department will decide whether or not to grant removal from the list.
8.See the Notice by the Ministry of Commerce on Soliciting Public Opinions on the Measures for Foreign Investment Information Reporting (Draft for Comments) on November 8, 2019.
9.See Press Conference by Ministry of Commerce and State Administration for Market Regulation Officials on Issues Concerning the Measures: http://www.mofcom.gov.cn/article/ae/sjjd/202001/20200102927607.shtml.
10.We noticed that the system of foreign investment information reporting has been embedded in the enterprise registration systems in Beijing, Sichuan, Guangdong; some provinces and cities (i.e. Shanghai) still retain independent websites for reporting.
11.Please refer to the questions answered by the heads of the relevant departments and bureaus of the Ministry of Commerce and the State Administration for Market Regulations in the “Measures for Foreign Investment Information Reporting”: http://www.mofcom.gov.cn/article/difang/202001/20200102928338.shtml.
12.For example, when setting up a foreign investment enterprise in Shanghai, investors need to submit information reports online and record a code generated by the system, and inform the administration for market supervision the code when applying for registration.
13.According to the Law of the People's Republic of China on Assets Appraisal, asset appraisal shall mean the professional services provided by appraisal organizations and their appraisal professionals as entrusted for the assessment and appraisal of immovable, movable, intangible assets, enterprise value, asset losses or other economic interests and the issuance of an appraisal report thereto; according to the definition of the China Audit Society, audit refers to the act of independently examining the accounting records and supervising the authenticity, legality and efficiency of financial revenues and expenditures.

.jpg)