24 June 2021
To download the guide, please click here.
To see other released IP Litigation & Enforcement guides on separate jurisdictions, please click here.
Is your jurisdiction a common law or civil law jurisdiction?
Civil law jurisdiction.
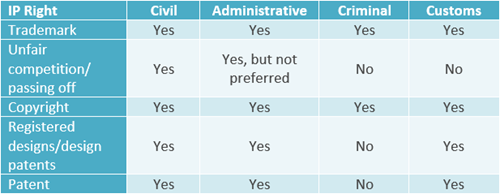
What methods are there for enforcing IP rights in your jurisdiction?
What courts have jurisdiction to handle civil IP cases?
Commercial IP cases involving foreign factors come under the jurisdiction of provincial-level economic courts. Non-commercial matters involving foreign factors come under the jurisdiction of provincial-level civil courts. For commercial IP and non-commercial IP matters that do not involve foreign factors, district-level economic courts and district-level civil courts have jurisdiction, respectively.
Is there any bifurcation of proceedings? For example, for determining validity or damages?
In principle, Vietnamese courts can handle validity and infringement matters in the same proceedings. However, the courts usually defer to IP Office of Vietnam (“IP Vietnam”) for invalidation matters. In practice, to prolong a court action, the defendant usually files an invalidation action with the IP Vietnam during an infringement action before the court. The opinions are split among judges whether they must suspend the infringement action case until IP Vietnam decides on a patent invalidation request that the defendant has filed before the trial opened. In 2019, a provincial court refused to suspend the civil proceedings despite pending invalidation requests before IP Vietnam.
What are procedures for civil enforcement?
To initiate a civil action, the rights-holder must file a petition with all necessary documentation to the court within three years of the alleged date of infringement. The court will then check whether the petition satisfies the procedural requirements for filing. If so, the case will be accepted and the court will issue a notice for the advance payment of court fees, which must be paid within seven days. Upon receipt of payment, the court will continue to handle the case by holding mediation hearing, evidence disclosure hearings, and trial.
Is a power of attorney needed for civil action to be brought? If so what are the procedures and time lines?
Power of attorney (“POA”) is mandatory for civil action to be brought. The POA should be submitted along with the petition and must be notarised and legalised.
What is the average time to trial in a civil case?
By law, the courts are required to hold a trial after about two months to six months from the date the case is accepted. However, in practice, it usually takes between 12 and 18 months for a court to hear a case.
What is the language of the proceedings? Is there a choice of language?
The language used is Vietnamese. There is no choice of language.
Is it possible to apply for summary judgment?
There is no procedural device similar to summary judgment in Vietnam. The Vietnam Civil Procedure Code 2015, does provide for summary proceedings, but even such a case, the court would need to hold a trial before ruling on the case.
On what basis are interim injunctions granted?
The IPR holder is entitled to request that the Court apply an interim injunction in relation to goods suspected to be infringing IPRs and raw materials, materials and means for manufacturing and trading such goods if (i) there is a threat of irreparable damage to be suffered by the IPR holder; or (ii) there is a threat of disposal or destruction of suspected infringing goods and related evidence if they are not protected in time.
On what basis are permanent injunctions granted?
In general, the plaintiff can ask the courts to request the defendant to cease their infringement. If the courts agree with the infringement claim, they will grant a final injunction. The plaintiff should request for a broadly worded judgment to ensure a wide scope of applicability.
What appeal procedures are available from a first instance judgment?
A judgment of first instance may be appealed to a higher court within 15 days of the date of judgement. After accepting the notice of appeal, the first-instance court must give notice in writing to the appellant requesting the payment of the appellate court fee deposit. The appellant must pay the fee deposit within five days from receiving the court’s notice. Upon receiving payment, the first-instance court will forward the notice of appeal to the Appellate Court. The Appellate Court will issue a decision to bring the case to an appellate hearing after receiving the relevant documents from the first-instance court.
What are the procedures for criminal enforcement?
IP holders must file their complaint before the Economic Police first. The Police would then check the formality of the complaint and ask for verification of the complaint. If the evidence is sufficient, they will conduct a raid and, if there is sufficient evidence to prosecute, issue a decision to initiate legal proceedings against the infringers. The case will then be transferred to the People’s Procuracy. The People’s Procuracy will review the case files and decide whether they should issue an indictment and submit the case to the criminal court. The court will review the received files and determine whether to bring the case to trial and hold hearings.
What are the procedures for criminal appeals?
A criminal judgement of first instance may be appealed to a higher court within 15 days of the date of judgment. After accepting the notice of appeal , the first-instance court must review it and forward it to other government agencies, including the People’s Procuracy and the Appellate Court. The Appellate Court will review the received files, forward them to the People’s Procuracy at the same level, and decide whether they would issue a decision to bring the case to trial and hold hearings.
What are the procedures for administrative enforcement?
To take administrative actions, IPR holders (or their authorised representatives) shall file written requests for the handling of the infringing acts to the competent authorities. The request must include evidence on the IPR holders’ status and evidence to demonstrate the alleged infringement. The competent authorities will examine the written request from IPR holders. If the IP infringement is established, the competent authorities will issue sanction decisions against the infringers. Administrative sanctions may include warnings or orders to terminate of the infringing acts. The administrative authorities cannot award damages.
What are the measures for Customs border protection?
Customs measures for protection of IP include suspension of customs procedures for suspected infringing goods, and inspection and supervision for detecting goods with signs of IP infringement. Right holders may file customs recordals with General Department of Vietnam Customs. Upon filing of a valid request, Vietnam Customs may take action against suspected infringing goods. They will usually take action if there is clear evidence that the goods are counterfeits of poor quality or may harm Vietnamese culture and society.
What IP treaties is your jurisdiction a member of?
-
Madrid Agreement
-
Madrid Protocol
-
Hague Agreement
-
WTO – TRIPS Agreement
-
Berne Convention
-
Paris Convention
-
Rome Convention
-
Patent Cooperation Treaty
Further reading:
Guides:
Articles:
-
Vietnam: Improving IP protections to attract fresh EU investment
-
Protection of coloured vs non-coloured trade mark in Vietnam
-
A consolidated view on the Technology Transfer Law and Practice of Vietnam
-
What you need to know to implement the EU-Vietnam Free Trade Agreement (EVFTA)
yvu@rouse.com


.jpg)