Does your jurisdiction use the common law system or the civil law system?
Continental Law.
What are the legal avenues for intellectual property rights protection in your jurisdiction?
| intellectual property | civil | administrative | criminal | customs |
| trademark | Yes | no | Yes | Yes |
| Unfair Competition/Counterfeiting | no | no | no | no |
| copyright | Yes | no | Yes | Yes |
| Registered design/design patent | Yes | no | Yes | no |
| patent | Yes | no | Yes | no |
Which courts have the power to adjudicate civil IP cases?
Intellectual property civil cases should be brought in commercial courts. The Commercial Court is a specialized court at the first instance level, which handles cases related to bankruptcy, bank liquidation, and intellectual property. An application for appeal should be made to the Supreme Court. Jurisdiction in tort depends on the defendant’s domicile.
Currently, there are five (5) commercial courts in Indonesia. Pursuant to Presidential Decree No. 97 of 1999, the commercial courts have territorial jurisdiction as follows:
| Commercial Court | province |
| Jakarta Center | Jakarta, West Java, Lampung, South Sumatra, West Kalimantan |
| Surabaya | East Java, South Kalimantan, Central Kalimantan, East Kalimantan, Bali, West Nusa Tenggara, East Nusa Tenggara |
| Semarang | Central Java and Yogyakarta |
| Medan | North Sumatra, Riau, West Sumatra, Ben Guru, Jambi, Aceh Special Region |
| Makassar(Former name: Ujung Pandang) | South Sulawesi, Southeast Sulawesi, Central Sulawesi, North Sulawesi, Maluku, Irian Jaya |
If the right holder resides outside Indonesia, the case must be filed with the Commercial Court of Central Jakarta.
Are there any procedural distinctions? For example: adjudicating the validity of intellectual property rights or adjudicating damages for infringement?
Issues of validity and infringement can be heard by the same tribunal (Commercial Court). In response to a patent infringement lawsuit, a patent invalidation counterclaim can be filed. However, it should be noted that if the relevant patent is still within nine months after the patent grant date, an application for patent invalidation must be filed with the Patent Appeal Board of the Patent Office. That is to say, the Commercial Court does not have jurisdiction over an application for patent invalidation until nine months have elapsed from the date of grant of the patent.
What are the procedures for civil litigation?
Civil cases should be brought to the commercial court of the IP infringer’s place of residence. However, a civil lawsuit may not be the best option for an anti-counterfeiting case. The most important significance of civil litigation is to establish precedents for major infringement cases. For example: trying difficult or complex trademark cases.
Do I need a Power of Attorney to file a civil lawsuit? If so, what are the specific procedures and timelines?
Yes, a power of attorney is required. A power of attorney, notarized and authenticated by the embassy or consulate, must be prepared when prosecuting. Now, a copy of the document certifying that the signatory of the Power of Attorney is authorized to sign is also required, but the copy must be notarized and certified by the embassy or consulate.
What is the average trial time for a civil case?
Intellectual property civil cases are usually completed within the statutory time limit. Patent cases are generally completed within six months. Other intellectual property cases were heard within three months.
What language are the proceedings in? Can I choose a language?
Proceedings are in Indonesian. Indonesian courts do not accept other languages.
Can I apply for summary judgment?
In Indonesia, there is no summary judgment system.
What are the grounds for granting a temporary injunction?
In addition to preventing the entry of suspected goods and preserving evidence, a preliminary injunction can be applied to ensure that the aforementioned evidence is not removed.
While interim relief can be granted by law, it has only been granted in one case so far, and that case was overturned on appeal. Therefore, it is difficult in practice to assess the chances of obtaining such relief.
What are the grounds for granting a permanent ban?
After the infringement is proven, the court usually grants an injunction to stop the infringement. In addition, the court will grant a permanent injunction even if the damages claim is dismissed due to the plaintiff’s failure to prove the loss suffered, if the infringement is proven to be true.
What are the appeal procedures for first instance judgments?
Those who disagree with the judgment of the Commercial Court may appeal to the Supreme Court.
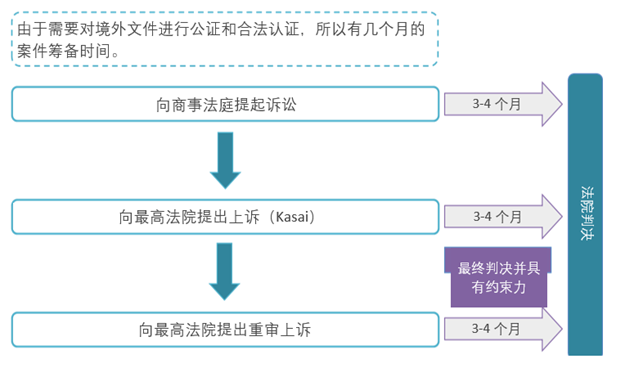
Grounds for appeal:
1. Grounds for appeal against original judgment:
If the lower court:
- incapable of hearing or beyond its competence;
- Improper application of law or violation of applicable law;
- The conditions prescribed by law were not met so that the relevant judgment could be set aside.
( Article 30 of the Supreme Court Act No. 14 of 1985 )
2. Grounds for retrial appeal:
- If, after the judgment is made, it is found that the judgment was made on the basis of a lie or deceit, or on evidence declared to be false by a criminal judge;
- If, after the judgment, important evidence that was not previously discovered is discovered;
- If the judge makes an order on a matter not claimed, or beyond the plaintiff’s claim;
- if a portion of the claim is not decided without consideration of the cause;
- If it is the same party, on the same grounds, the same court or other court at the same level has made a conflicting judgment in a case on the same matter;
- If the judge is negligent or manifestly wrong.
( Article 67 of the Supreme Court Act No. 14 of 1985 )
What are the procedures for criminal rights protection?
For crimes related to intellectual property infringement, the intellectual property owner must submit a formal complaint to the relevant authorities to trigger criminal rights protection procedures. Based on the complaint, the police will launch a criminal investigation, including the collection or seizure of relevant evidence. However, police enforcement is not entirely clear and transparent, which may lead to inconsistencies in the practice of seizures, such as differences in timing. After police action, the IP holder can reach a settlement with the infringer or continue with criminal prosecution.
What are the procedures for criminal proceedings?
The District Court is responsible for adjudicating criminal cases. Those who are not satisfied with the judgment of the district court shall appeal to the high court with the same territorial jurisdiction as the original district court.
The parties have the right to appeal the judgment unless otherwise provided ( section 21(1) of the Judiciary Act No. 4 of 2004 ). The decision of the High Court can be further appealed to the Supreme Court. Supreme Court decisions are final and binding, but are subject to judicial review in certain circumstances.
An application for appeal can be lodged with the High Court within 7 days of the District Court’s decision. The High Court must make a judgment within 3 months of receiving the application for appeal. Within 14 days after the judgment of the High Court, those who are dissatisfied with the judgment may submit an appeal to the Supreme Court.
Grounds for appeal:
The law does not provide specific grounds for appeal. A final binding judgment cannot be appealed (a judicial review can be brought, but this is not technically an act of appeal).
What are the procedures for administrative rights protection?
There are no administrative remedies in Indonesia.
What are the measures for customs border protection?
Trademark and copyright holders can submit customs filing applications that enable customs officers to detain goods they believe are suspected of being counterfeit. The applicant for customs filing can only be the right holder of Indonesian nationality. Customs filings are only valid for one year, but can be renewed for an additional year.
What intellectual property treaties are there in your jurisdiction?
- Madrid Agreement
- WTO Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights
- WIPO Performances and Phonograms Treaty
- World Intellectual Property Organization Copyright Treaty
- World Intellectual Property Organization Trademark Law Treaty
- Berne Convention
- Paris Convention
- Patent Cooperation Treaty
Other information
Guides:
- Intellectual Property Guide: Online E-Commerce Shopping Platforms in Southeast Asia – Indonesia
- Be aware of the gap between intellectual property protection laws and the actual situation of intellectual property in Indonesia
- E-Commerce Intellectual Property Enforcement in Southeast Asia
- What is “hijacking”? !
- The most challenging e-commerce platform in Southeast Asia
- Overview of patent protection in four major ASEAN countries
- Electronic filings and hearings in Southeast Asian courts
- Indonesian Patent Litigation: An Overview
Articles:
- Indonesia: New Amendments to Intellectual Property Laws
- Government Compulsory Licensing in Indonesia
- Digital Transformation in Indonesia
- Indonesia: Regulations for the Implementation of the Employment Creation Law
- Indonesia: New Comprehensive Law on Job Creation and New Amendment to Intellectual Property Law

For further information, please contact:
Kin Wah Chow, Principal, Rouse
kchow@rouse.com





